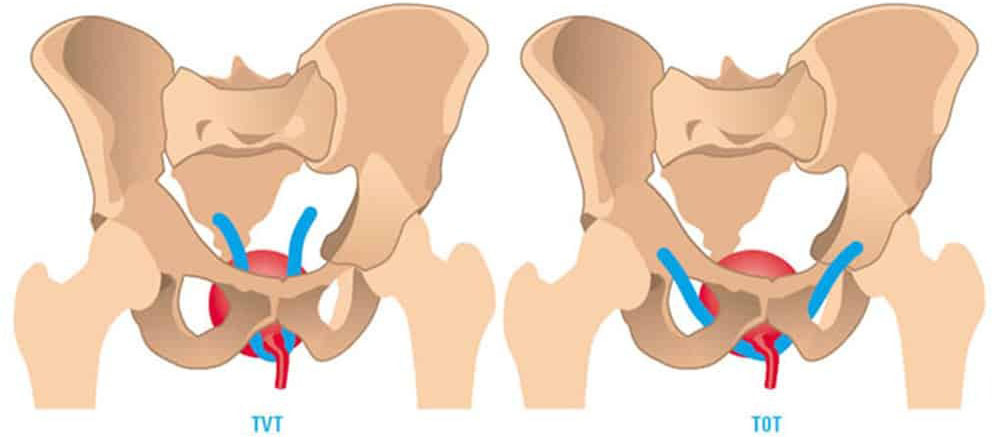
The bladder, commonly referred to as the urinary bladder or urinary sac, is the area where urine from the kidneys is stored. The contraction and relaxation of the bladder muscles are controlled by the nerves in the area and the brain. As the bladder fills, it expands, and the muscles at the lower end of the bladder help keep the opening closed. Urinary incontinence, medically known as urinary incontinence, refers to the inability to control urination, resulting in involuntary leakage.
Urinary incontinence affects 15-30% of women aged 65 and older, and up to 50% of those receiving home nursing care. This condition can have a significant impact on women's social, clinical, and psychological well-being. There are different types of urinary incontinence, including genuine stress incontinence, urgency incontinence, overflow incontinence, mixed incontinence, and incontinence caused by anatomical abnormalities in the urinary tract.
Depending on the cause of the condition, gynecologists, urologists, and neurologists can assist in managing this issue. Before visiting a doctor, it is recommended to keep a diary for at least two days, recording the frequency and intensity of urination and the number of episodes. The patient's symptoms, including their details, duration, frequency, and severity, will also be gathered through a questionnaire.
During the diagnosis and treatment phases, various methods can be employed.
In non-surgical treatments, the goal is to address the underlying causes of urinary incontinence. Pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises) are highly effective in strengthening the pelvic floor muscles and managing urinary incontinence.
Bladder training aims to establish a habit of visiting the toilet at specific intervals. This method is typically recommended for individuals with urgency incontinence or urge-related leakage.
Electrical stimulation is a technique that uses low-level electrical currents to stimulate the pelvic floor muscles. This approach may help strengthen the muscles and improve control.
For more detailed information on urinary incontinence, please refer to the related section on our website.