With advances in medicine, many surgical procedures can now be performed using less invasive, more comfortable methods that allow faster recovery, instead of traditional open surgeries. In the field of women's health, laparoscopy is widely used both for diagnosis and treatment purposes.
This article covers what laparoscopy is, which women's health conditions it is preferred for, its advantages, risks, and the recovery process in detail.
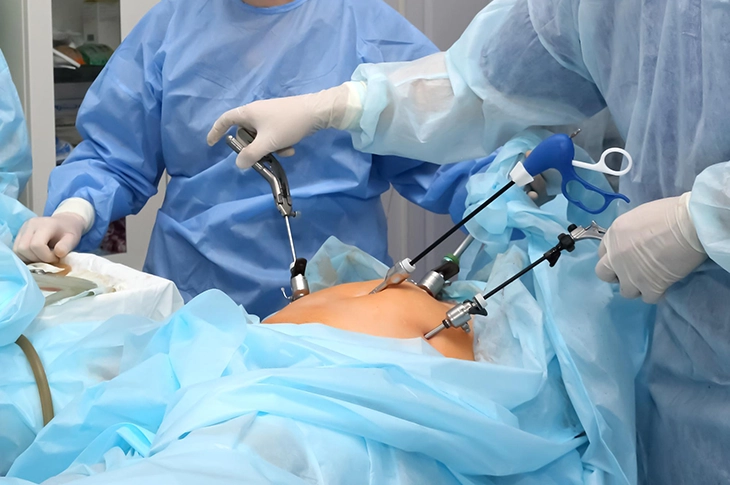
What is Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is a procedure where a few small incisions of 0.5–1 cm are made in the abdominal area, and special cameras and surgical instruments are used to visualize internal organs and perform necessary surgical interventions. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
During the procedure, the abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to allow the surgeon a clearer view of all structures.
When is Laparoscopic Surgery Used?
For Diagnostic Purposes:
- Evaluation of intra-abdominal adhesions
- Investigation of infertility causes
- Determining the source of pelvic pain
For Therapeutic Purposes:
- Surgery for endometriosis
- Removal of ovarian cysts (cystectomy)
- Myomectomy (removal of fibroids)
- Removal or opening of fallopian tubes (salpingectomy/tubal reanastomosis)
- Removal of the uterus (laparoscopic hysterectomy)
- Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
- Tubal ligation (fallopian tube tying as a birth control method)
Advantages of Laparoscopy
- Small incisions, minimal scarring
- Better cosmetic results
- Almost no suture marks
- Less pain
- Less damage to muscle tissue, resulting in higher post-operative comfort
- Faster healing
- Usually 1–2 days hospital stay
- Return to daily activities within 5–7 days
- Lower risk of infection and bleeding
- More delicate handling of organs
- Especially advantageous in cases like endometriosis where tissue preservation is important
- Less damage to ovarian reserve
- Important for women planning pregnancy